人工智能作业 使用AStar算法解决八数码问题
八数码问题是一个经典的搜索问题,本文将介绍如何使用启发式搜索—— AStar 算法来求解八数码问题。
使用AStar算法解决八数码问题
问题描述
八数码问题的A星搜索算法实现
要求:设计估价函数,并采用c或python编程实现,以八数码为例演示A星算法的搜索过程,争取做到直观、清晰地演示算法,代码要适当加注释。
八数码难题:在3×3方格棋盘上,分别放置了标有数字1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8的八张牌,初始状态S0可自己随机设定,使用的操作有:空格上移,空格左移,空格右移,空格下移。试采用A*算法编一程序实现这一搜索过程。
算法描述
预估值的设计
A* 算法的花费为 f(n) = g(n) + h(n),其中 g(n) 为搜索深度,定义为状态单元 state 的成员变量,在每次生成子节点时将其加一。h(n) 为不对位的将牌数,将该部分的计算重载于 state 的小于运算符中,并将 f(n) = g(n) + h(n) 的值作为状态单元的比较值。
数据结构设计
- 每个状态用一个结构体表示,其中 depth 为状态深度,str 为该状态字符串,并重载小于运算符用于计算最优。
- open 表使用优先队列
priority_queue,实现在 O(logn) 的时间复杂度内获取最优值。 - close 表使用哈希集合
unordered_set,实现在 O(1) 时间复杂度内判断某状态是否已位于 close 表中。 - 而为了得到最优搜索路径,还需要将每个状态的前驱加以保存,前驱表 pre 我使用了哈希表
unordered_map,模板类型为pair<string, string>,表示 key 的前驱为 value。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
private:
static string targetStr;
const vector<vector<int>> dirs = { {-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1} }; // 四个移动方向
struct state
{
string str;
int depth;
state(string s, int d) : str(s), depth(d) {}
bool operator < (const state& s) const {
int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
if (s.str[i] != targetStr[i])
++cnt1;
if (this->str[i] != targetStr[i])
++cnt2;
}
return cnt1 + this->depth > cnt2 + s.depth; // f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
}
};
inline void swapChr(string& child, int iniInd, int childInd) { // 交换字符,完成移动
child[iniInd] = child[childInd];
child[childInd] = '0';
}
void printPath(unordered_map<string, string>& pre, string path) { // 输出路径
stack<string> st;
while (path != "None") {
st.emplace(path);
path = pre[path];
}
int cnt = 0;
while (++cnt && !st.empty()) {
string str = st.top();
st.pop();
cout << "step" << cnt << ": " << str.substr(0, 3) << endl
<< " " << str.substr(3, 3) << endl << " " <<
str.substr(6, 3) << endl << string(15, '-') << endl;
}
}
public:
void eightDigitalQues(const string& ini, const string& target) {
targetStr = target;
priority_queue<state> open;
unordered_set<string> close;
unordered_map<string, string> pre;
open.emplace(ini, 0);
pre[ini] = "None";
while (!open.empty()) {
string n = open.top().str;
int d = open.top().depth;
open.pop();
close.emplace(n);
if (n == target) {
break;
}
int iniInd = n.find('0');
int x = iniInd / 3, y = iniInd % 3;
for (const auto& dir : dirs) { // 尝试选择四个方向
int nx = x + dir[0], ny = y + dir[1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx <= 2 && ny >= 0 && ny <= 2) { // 满足移动后下标满足条件
int childInd = nx * 3 + ny;
state childState(n, d + 1);
swapChr(childState.str, iniInd, childInd);
if (close.count(childState.str)) // 如该状态已加入close表,则跳过
continue;
open.emplace(childState); // 加入满足条件的子状态
pre[childState.str] = n; // 更新前驱
}
}
}
printPath(pre, target); // 输出流程
return;
}
};
string Solution::targetStr;
int main() {
Solution S;
string ini, target;
cin >> ini >> target;
S.eightDigitalQues(ini, target);
cin.get();
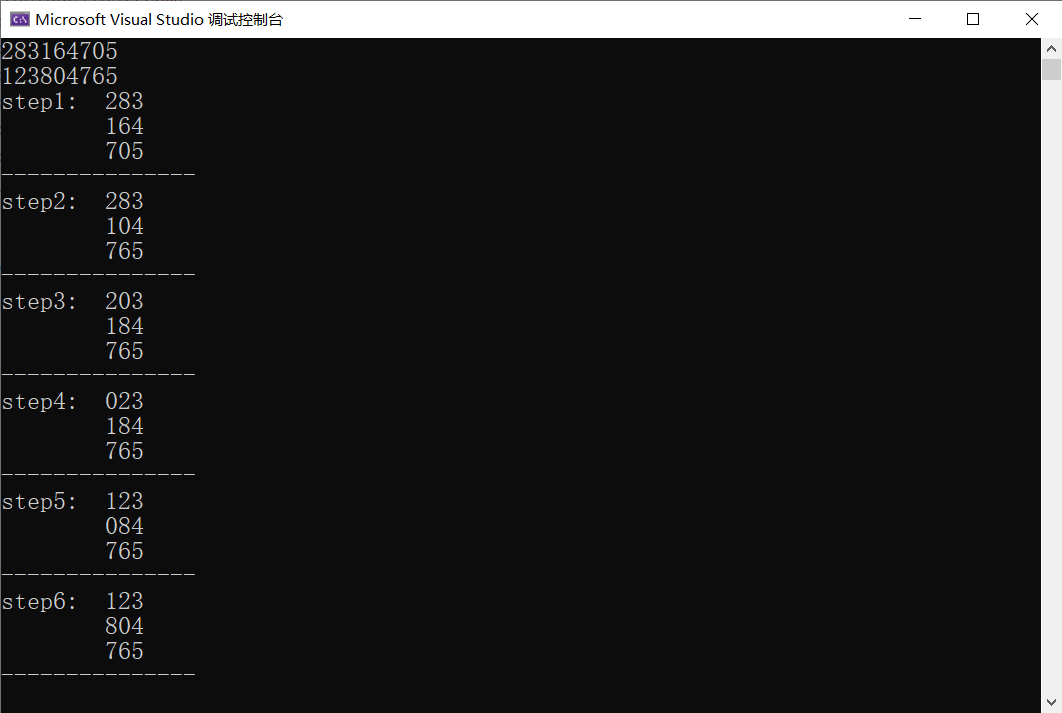
}运行结果
输入
原状态:283164705, 目标状态:123804765
输出
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 Lordaeron_ESZ's blog!
评论













